Swing Trading vs. Day Trading: Understanding the Differences and Benefits
Swing Trading vs. Day Trading: Understanding the Differences and Benefits
In the world of trading, where all is lost and gained in a split second, risk management is a key value. Loss of capital has always been a big fear for the newbies in this task. Therefore, as they explore the intricacies of the market, risk management becomes more and more evident.
This blog addresses this crucial matter by expounding on two well-known trading approaches, which are swing trading and day trading. By grasping these disparities, you can better determine which trading style suits your objectives, risk tolerance, and personal preferences.
Overview Swing and Day Trading
Comparing Strategies
Risk Management and Psychological Considerations
Lifestyle and Time Investment
Performance Evaluation and Profit Potential
Closing Thoughts

What is Swing Trading
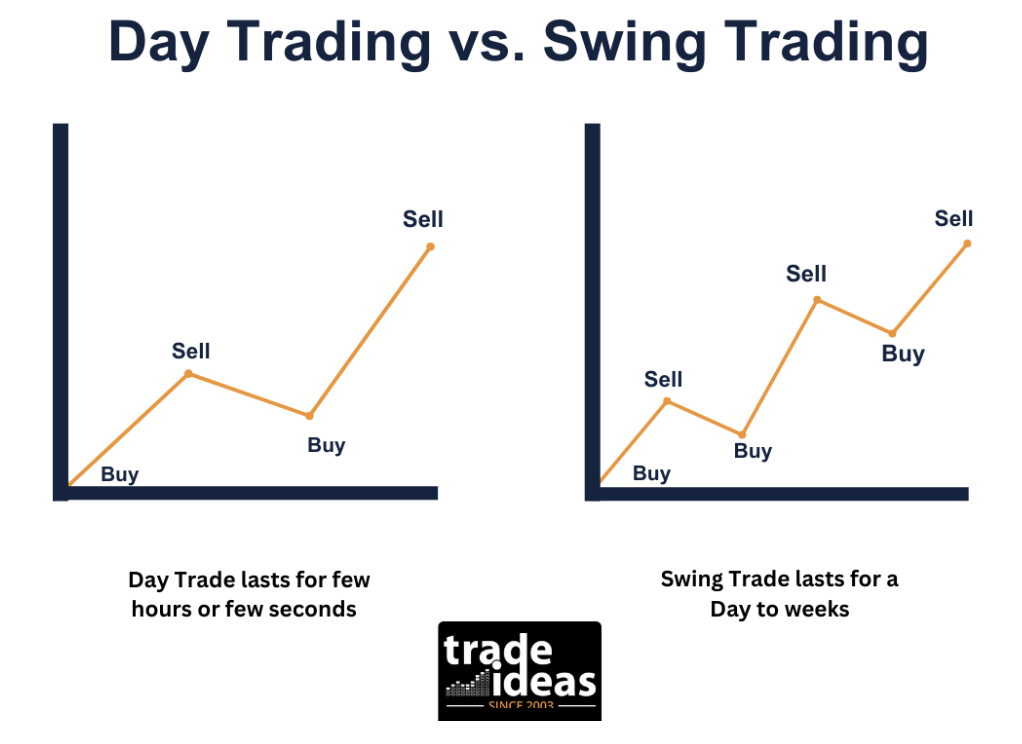
Swing trading is a trading style where you buy and hold stocks, currencies, or other financial instruments for some time. This period is usually a few days to a few weeks. The goal is to profit from the price swings that happen in the market over this time frame.
What is Day Trading
Day trading is a trading style where you buy and sell financial instruments within the same trading day. You don’t hold any positions overnight. Day traders try to make profits from the small price movements that happen throughout the day. They use charts and technical indicators to identify buying and selling opportunities.
Day trading requires continuous market monitoring and the ability to make quick, well-timed decisions. It carries a higher short-term risk because of the frequent trades and reliance on intraday price movements.
Comparing Trading Strategies: Swing vs. Day
Swing trading and day trading are two popular short-term approaches, each with distinct methods, risks, and capital requirements. Understanding their differences helps traders choose the strategy that best fits their goals, resources, and tolerance for risk.
A. Swing Trading: Methodical Precision
This analogy effectively captures the essence of swing trading, a method centered on holding positions for weeks to months.
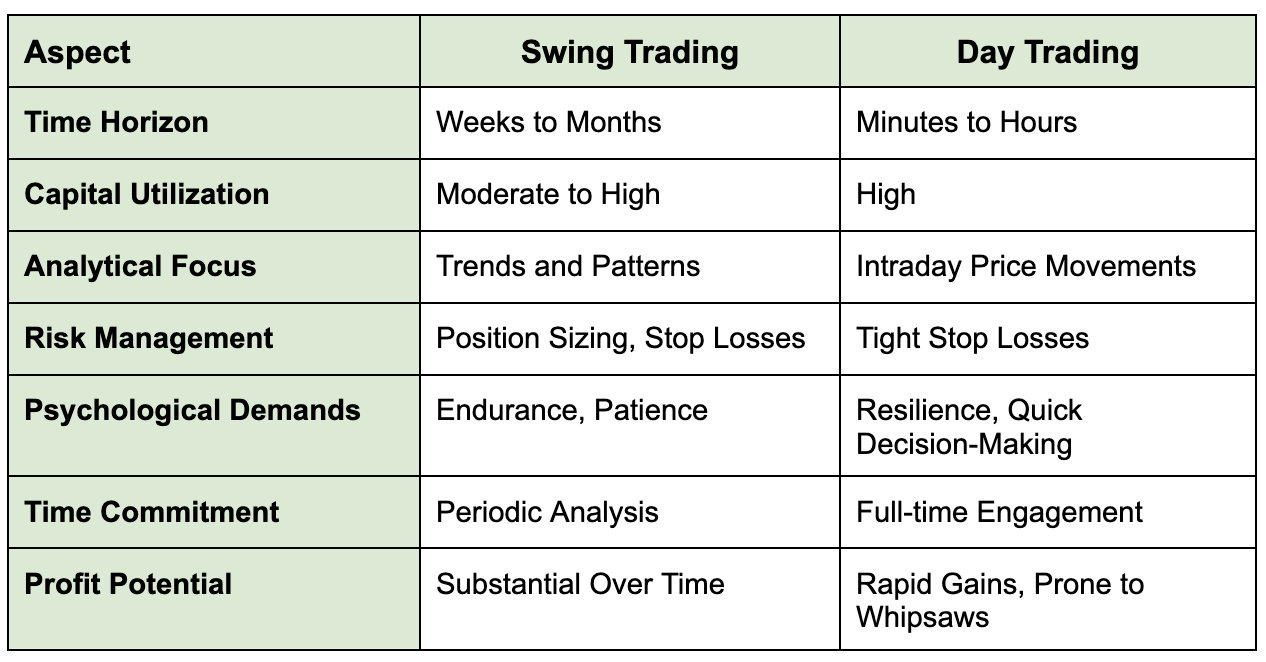
- Time Horizon: Positions are usually held for a few days to 2–4 weeks, respectively, aiming to capture medium-term trends and price swings.
- Capital Usage: Requires moderate capital to absorb potential losses resulting from overnight market movements and changing market conditions.
- Analytical Focus: Strong focus on technical analysis (trendlines, support/resistance, patterns), sometimes supported by fundamentals. A clear risk management plan is needed to balance gains against acceptable risks.

B. Day Trading: Adrenaline-Fueled Rush
When it comes to day trading, speed is of the essence. It’s like participating in a paced race where every second matters. Day traders thrive on seizing opportunities within a trading day by capitalizing on intraday price movements.
Time Horizon: Trades last from minutes to several hours and are always closed before the market session ends to reduce operational risk.
Capital Usage: Requires larger capital and margin access, since small intraday moves can quickly lead to financial losses without strict controls.
Analytical Focus: Relies on real-time charts, momentum, and order flow. Traders must excel in risk identification and managing risk with stop-losses and contingency plans to protect the bottom line.
Choosing Between Swing Trading and Day Trading
Both swing trading and day trading can be effective, but their success depends on discipline, informed decisions, and structured risk reduction.
- Swing trading fits those who prefer a more methodical approach to risk and can wait for setups over several days.
- Day trading may suit traders who are comfortable with higher strategic risk and the need for immediate execution.
- In both cases, evaluating strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats is key to long-term success.
Neither strategy eliminates potential threats; success depends on preparation, sufficient capital, and a well-structured risk management plan.
Risk Management and Psychological Considerations
Effective risk management and a resilient mindset are crucial components of swing and day trading. However, the strategies employed and psychological demands vary between the two approaches.
Swing Trading: Discipline and Patience
- Swing traders focus on setting appropriate position sizes and applying stop-loss orders effectively. This helps limit potential losses while allowing market trends time to develop. Some also use risk transfer strategies, such as diversifying across different assets or sectors.
- Emotional Resilience: Swing trading demands a particular type of emotional resilience from traders. Maintaining composure during periods of uncertainty and sticking to a predetermined trading plan is crucial.
Swing traders need to have the strength to endure tough times and stick to their trading strategies with discipline. Assessing strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities in both their trading approach and the products or services they trade can provide an additional edge.
Day Trading: Composure Under Pressure
- Stringent Risk Management: Day traders place importance on managing risks. They heavily rely on stop-loss orders and precise position sizing to control losses caused by price changes that can happen within a trading day. Their approach to risk often involves tight controls and contingency measures to guard against sharp losses.
- Emotional Strength: The rapid pace of day trading requires a level of strength. Day traders must stay composed under pressure, handle stress, and make decisions without giving in to emotional impulses.
Lifestyle and Time Investment
Trading success and well-being are influenced by lifestyle and time commitment. Traders need to set their objectives and preferences. Balancing the analysis of market dynamics while catering to other obligations requires proper time management. It is through maintaining a balance between personal life and business that stress can be avoided, as well as burnout, hence long-term trading viability is ensured.

By focusing on a balanced approach between trading and personal life, traders can make informed decisions, protect against different types of risk, and build a rewarding practice that strengthens both earnings and overall quality of life.
A. Swing Trading: Finding the Right Balance
- Flexibility is key: Swing trading provides a level of flexibility that suits individuals who trade part-time or have commitments. While staying on top of market analysis is important, swing traders can adjust their positions, which allows them to trade at their convenience.
- Time Commitment: Swing traders dedicate time periodically to analyze the market, monitor their positions, and make adjustments. This time commitment, although significant, is usually less demanding compared to the schedule of day trading.
B. Day Trading: Full-Time Engagement
- Demanding Schedule: Day trading demands full-time dedication since traders must be actively involved during market hours. Balancing this demanding schedule with responsibilities can be quite challenging.
- Constant Alertness: Day traders need to monitor and execute trades on time. Their ability to manage strengths, weaknesses, and opportunities while controlling losses directly impacts results and their long-term sustainability.
Performance Evaluation and Profit Potential
Although both swing trading and day trading offer profit potential, the methods for evaluating performance and achieving gains differ significantly.
Swing Trading: Term Mindset
Comparison with Market Indices and Peers: Swing traders often evaluate their performance by comparing it against market indices and industry peers. They focus on capturing medium-term trends and generating returns.
Potential for Substantial Returns Over Extended Periods: Swing traders have the potential to achieve returns by consistently building on their gains through careful and disciplined trading.
Day Trading: Sprinter’s Sprint
Day traders, on the other hand, keep an eye on their daily performance to quickly assess and adjust their strategies for better results. This immediate feedback loop allows them to make changes as needed.
While day trading can lead to profits by taking advantage of short-term price movements, it also comes with the risk of reversals that can result in losses if risk management is not properly implemented.
To distinguish between swing trading and day trading, let’s compare some aspects in a table.
Swing Trading vs. Day Trading: Choosing the Right Approach
The choice between swing trading and day trading ultimately depends on your goals, risk tolerance, and lifestyle. Each approach offers distinct advantages and challenges, making it essential to understand market dynamics, apply sound risk management, and maintain psychological discipline.
Swing trading suits those who prefer a structured approach to capturing medium-term trends while balancing other commitments. Day trading, by contrast, requires full-time focus, rapid decision-making, and comfort with short-term volatility.
Whichever path you choose, long-term success comes from disciplined execution, continuous learning, and aligning your strategy with your personal strengths and circumstances. Approach the markets with preparation and resilience, and you’ll be better positioned to navigate risks and seize opportunities.

FAQs on Swing Trading vs. Day Trading
1. Which trading approach is recommended for beginners?
While both swing trading and day trading demand commitment and a good grasp of market trends, swing trading is often seen as beginner-friendly. Swing traders hold their positions for longer periods than intraday traders do, giving beginners enough time to study and perfect their trading methods at a slower pace.
It’s a method where beginners can acquire skills in analyzing market trends, risk management techniques, and making decisions on trade without necessarily having to spend their entire day monitoring the markets.
2. How much money is needed to start swing trading or day trading?
Capital requirements can differ depending on preferences, risk tolerance, and trading tactics. Generally speaking, day trading may need capital due to higher capital usage and the potential for quick losses. Swing trading can be started with capital, but it’s important to have enough funds to withstand potential downturns.
3. Is it possible to blend swing trading and day trading into a combined strategy?
Yes, it’s feasible to merge swing trading and day trading into a strategy. Some traders opt to engage in swing trading for positions while also dabbling in day trading activities for instruments or markets. This strategy allows traders to vary their approaches and benefit from both term and medium-term opportunities.
