Income / Debt Ratio
Table of Contents
- Understanding the Income Debt Ratio Filter
- Income Debt Ratio Filter Settings
- Using the Income Debt Ratio Filter
- FAQs
Understanding the Income Debt Ratio Filter
The income/debt ratio is a financial metric used to assess a company's financial strength and leverage by comparing its income to its total debt. Here's a detailed explanation of the "Income/Debt Ratio" filter:
Definition: The income/debt ratio measures the relationship between a company's income and its total debt. It is calculated by dividing the company's income (such as net income or operating income) by its total debt. The formula for the income/debt ratio is: Income / Debt
This ratio provides insights into the company's ability to generate income relative to its debt obligations.
Interpretation:
Larger Value: A higher income/debt ratio indicates that the company generates more income relative to its total debt. This suggests that the company has sufficient income to cover its debt obligations comfortably, reflecting strong financial health and lower leverage. A larger value is generally viewed positively as it indicates a lower degree of financial risk associated with debt.
Smaller Value: Conversely, a lower income/debt ratio suggests that the company's income may be insufficient to cover its debt obligations adequately. This indicates higher leverage and may raise concerns about the company's ability to service its debt payments, especially during periods of financial stress or economic downturns. A smaller value implies higher financial risk and potential vulnerability to debt-related challenges.
Income Debt Ratio Filter Settings
Configuring the "Income/Debt Ratio" filter is simple and can be done within the Window Specific Filters Tab of the Configuration Window in your Alert/Top List Window.
Here's how to set up the filter in your configuration window:
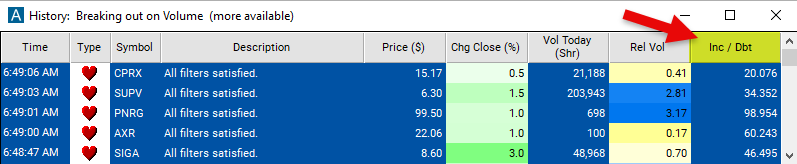
- Set the minimum value to 20 to see only stocks with an income/debt ratio of 20/1.
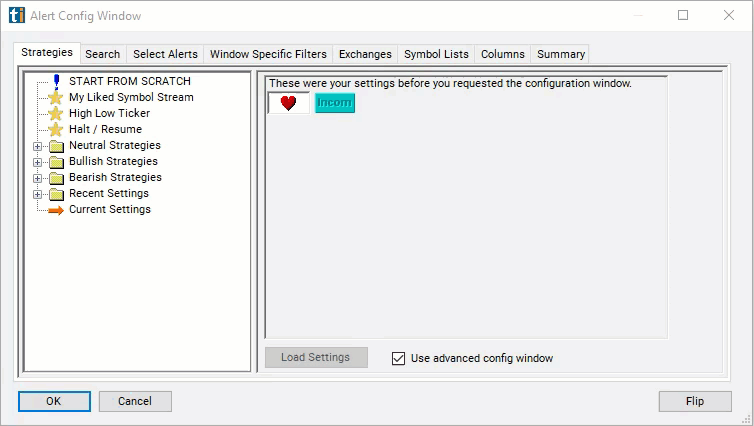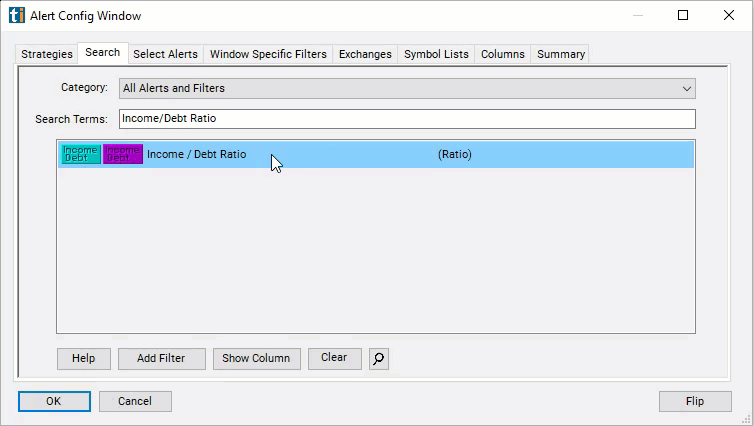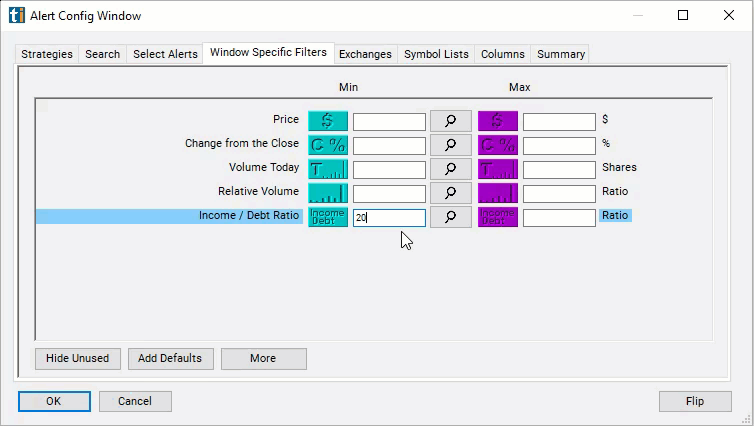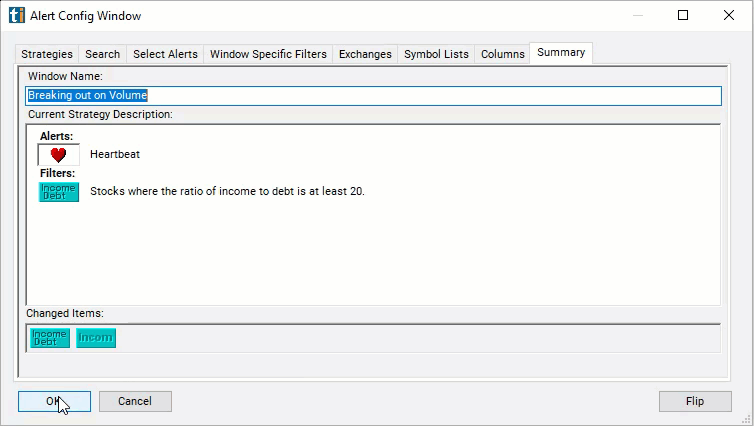
Using the Income Debt Ratio Filter
The "Income/Debt Ratio" filter can be used in various trading strategies, including:
Leverage Analysis: Traders can use the income/debt ratio to assess a company's leverage level and financial health. By comparing the income/debt ratios of different companies within the same industry or sector, traders can identify companies with lower leverage and potentially lower financial risk. Trading strategies may involve buying stocks of companies with higher income/debt ratios and selling short stocks of companies with lower ratios, betting on relative strength or weakness in leverage.
Sector Rotation: Traders may employ sector rotation strategies based on income/debt ratios. They can identify sectors or industries with companies exhibiting strong income/debt ratios and allocate capital accordingly. Sector rotation strategies involve shifting investments into sectors with favorable income/debt ratios and away from sectors with weaker ratios, aiming to capitalize on trends in financial health and leverage across industries.
Quality Investing: Quality investing strategies focus on investing in high-quality companies with strong financial fundamentals, including healthy income/debt ratios. Traders may screen for stocks of companies with high income/debt ratios relative to their peers and industry averages. Quality investing strategies involve building a portfolio of fundamentally sound stocks with attractive income/debt ratios, aiming to achieve consistent returns over the long term.
FAQs
What does the income/debt ratio indicate?
- The income/debt ratio measures a company's financial strength and leverage by comparing its income to its total debt. A higher income/debt ratio indicates that the company generates more income relative to its debt obligations, suggesting stronger financial health and lower leverage. Conversely, a lower income/debt ratio may indicate higher leverage and potential financial risk associated with debt.
How is the income/debt ratio calculated?
- The income/debt ratio is calculated by dividing a company's income (such as net income or operating income) by its total debt. The formula for the income/debt ratio is: Income / Total Debt.
What is considered a favorable income/debt ratio?
- A favorable income/debt ratio is one where the company's income comfortably exceeds its total debt obligations. While there is no universal threshold for what constitutes a favorable ratio, a higher income/debt ratio relative to industry peers or historical averages is generally viewed positively, indicating lower leverage and stronger financial health.
How does the income/debt ratio affect stock trading decisions?
- Traders use the income/debt ratio as a fundamental metric to assess a company's financial strength and leverage. A higher income/debt ratio may signal a lower degree of financial risk associated with debt, making the company's stock more attractive to investors. Conversely, a lower income/debt ratio may raise concerns about the company's ability to service its debt obligations, potentially impacting its stock price.
Filter Info for Income / Debt Ratio [IncomeDebt]
- description = Income / Debt Ratio
- keywords = Fundamentals Changes Daily
- units = Ratio
- format = 3
- toplistable = 1
- parent_code =




